Which Best Describes the Action of Class Ii Antiarrhythmics
Metoprolol atenolol carvedilol and esmolol. The medications in this class include amiodarone dronedarone sotalol ibutilide dofetilide and bretylium.

Cardiac Arrhythmias Medical Pharmacology And Therapeutics 4e
Now beta blockers that mainly target pacemaker cells are actually classified as class II antiarrhythmics and just like all beta blockers they can be subdivided into selective beta-1 blockers like atenolol acebutolol betaxolol bisoprolol esmolol and metoprolol.

. Pace-Pacing Clinical Electrophysiology 175 Pt 2. When educating a group of nursing students on the mechanism of the action of various anti-arrhythmic drugs the nurse identifies which of the following drugs as inhibiting the beta. It also discusses some new studies providing insight into the mechanism of action of these drugs.
Class III antiarrhythmic agents eg amiodarone prolong the action potential and slow calcium channel blockers class IV suppress the calcium inward current and calcium-dependent action potentials. Which antiarrhythmic drugs alter the action potential and how is this evident in an ECG. Class II antiarrhythmics.
Competitive block beta receptor sites in the heart and kidneys. However some medications in this class also exert effects on Na channels calcium channels and adrenergic receptors. Class II antiarrhythmic drugs.
Antiarrhythmic drugs are used to. This in turn blocks phase 4 of action potential. All antiarrhythmic drugs directly or indirectly alter membrane ion conductances which in turn alters the physical characteristics of.
In this video we will discuss Class II anti-arrhythmic drugs also known as the beta blockers. The main mechanism of action includes blocking the cardiac K channels to prolong repolarization. Inhibit β-adrenergic activation of adenylate cyclase cAMP Ca 2 SA node and AV node activity.
Therefore attempts have been made to classify the different antiarrhythmic drugs so by mechanism. Competitive block beta receptor sites in the heart and kidneys Block potassium channels slowing the outward movement of potassium Block the movement of calcium ions across the cell membrane Block sodium channels in the cell membrane during an action potential. These drugs work as antiarrhythmics mainly by blocking beta-1 signaling at nodal tissue in the heart especially the AV node.
Alter the excitability of cardiac cells by changing the duration of the effective refractory period. Briefly describe the Vaughan-Williams antiarrhythmic classification system. Class 2 antiarrhythmics include beta-blockers which exert their therapeutic effects by blocking epinephrine and norepinephrine from binding to the beta-adrenergic receptors in cardiac tissue.
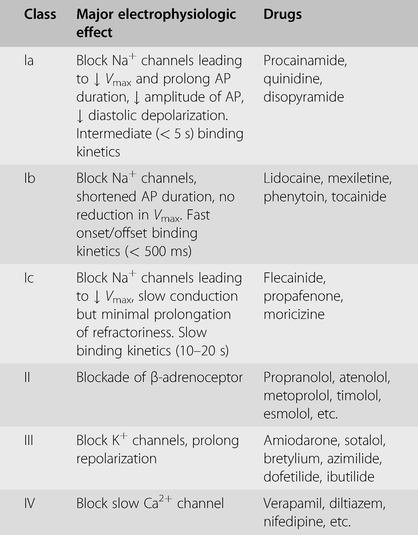
Class I - Na channel blockers Class II - beta blockers Class III - K channel blockers Class IV - Ca channel blockers Class V - others. Sodiumpotassium channel blockers Class IA and potassium channel blockers Class III increase action potential duration. Beta-adrenergic antagonists class II exert their effects by antagonizing the electrophysiological effects of beta-adrenergic catecholamines.
The outcome is an antiarrhythmic effect which results from decreased sinoatrial node activity and increased atrioventricular conduction time and. These work by blocking sympathetic nervous system stimulation to the heart thereby reducing the transmission of impulses within the hearts conduction system. This class interferes with action potential by blocking beta receptors in the heart and kidneys.
Competitive block beta receptor sites in the heart and kidneys A patient with cardiac arrhythmia is prescribed verapamil. The Class 2 antiarrhythmics describe beta-blockers that are used to treat arrhythmias of the heart in the acute setting. Class III antiarrhythmic drug action in experimental atrial fibrillation.
They reduce sympathetic modulation of AV node modulate calcium current and reduce calcium overload and delayed afterdepolarizations and reduce the. Class II antiarrhythmics are beta-adrenergic blockers. Differences in reverse use dependence and effectiveness between d-sotalol and the.
Class II antiarrhythmics engage in competitive inhibition of beta receptors specifically found in the heart and kidneys. Class I - phase 0 Class II - phase 4. Which best describes the action of class II antiarrhythmics.
Antiarrhythmic drugs comprise many different drug classes and have several different mechanisms of action. Decrease slope of phase 4 in cardiac pacemaker cells suppression of aberrant pacemakers. Class II antiarrhythmics inhibit beta-adrenergic activation of adenylate cyclase reduce intracellular cAMP levels and therefore reduce Ca2 influx resulting in decreased sinoatrial node SAN pacing and triggered activity and increase in atrioventricular node AVN conduction time and refractoriness.
We will begin by discussing their general mechanism of action. Or non-selective beta blockers like timolol and propranolol that target all beta receptors. Furthermore some classes and even some specific drugs within a class are effective with only certain types of arrhythmias.
Prolong AV node repolarization AV node is highly sensitive to beta blockers prolongation of PR interval. Conduction time through AV node is increased while contractility is diminished. Class II antiarrhythmics What is the pharmacology of beta blockers as antiarrhythmics.
Class I of antiarrhythmic adrugs is. Indications and limitations of class II and III antiarrhythmic drugs in atrial fibrillation. Decrease or increase conduction velocity.
Classes and their mechanisms of action. Class II Antiarrhythmic drugs. Which best describes the action of class II antiarrhythmics.
This review describes the latest developments in the clinical usage of class III antiarrhythmics. IV- Ca 2 channel blocker. Just like all other beta-blockers these drugs end with the suffix -lol as in.
Wong J Feng J Nattel S. New data suggest that amiodarone is one of the most effective drugs for management of ventricular as well as supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Class I antiarrhythmic drugs.
What phase of the action potential do each class of antiarrhythmics effect. Which best describes the action of class II antiarrhythmics. Based on their different effects on heart cells antiarrhythmic drugs are divided in to 5 classes by Vaughan-Williams classification.
II- beta adrenoceptor antagonist III- action potential prolongation usually K channel blocker. Decrease the slope of phase IV depolarization slowing the heart.
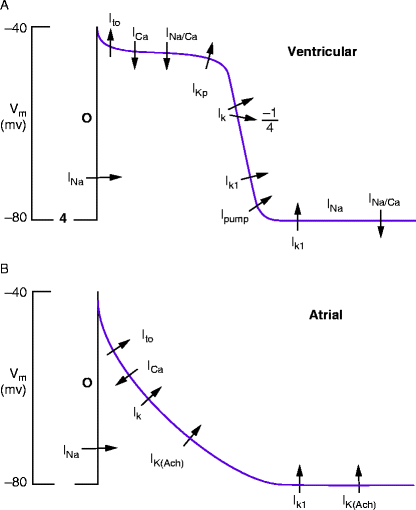
Antiarrhythmic Drugs Chapter 43 Anesthetic Pharmacology

Antiarrhythmics Mnemonic Medications Nursing Pharmacology Pharmacology Mnemonics

Antiarrhythmic Agent An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
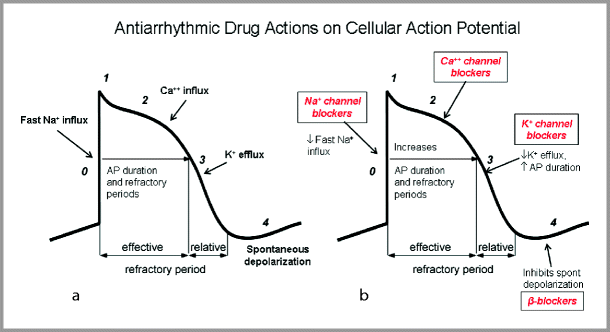
Antiarrhythmic Drug Management Springerlink

Pdf Modernized Classification Of Cardiac Antiarrhythmic Drugs
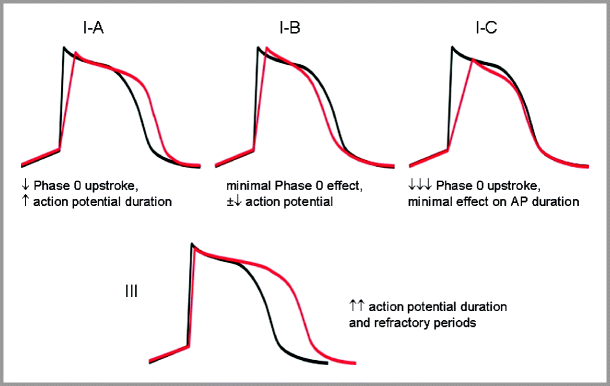
Antiarrhythmic Drug Management Springerlink

Cv Pharmacology Vaughan Williams Classification Of Antiarrhythmic Drugs

Pdf Classification And Choice Of Antiarrhythmic Therapies
Pdf Modernized Classification Of Cardiac Antiarrhythmic Drugs

Antiarrhythmic Drugs Drug Therapy Pocket Drug Guide

Pdf Pph 308 Medicinal Chemistry Ii Unit I Anti Arrhythmic Drugs

Pdf Modernized Classification Of Cardiac Antiarrhythmic Drugs

Pdf Classification And Choice Of Antiarrhythmic Therapies

Cardiac Action Potential And Antiarrhythmics Flashcards Quizlet



Comments
Post a Comment